
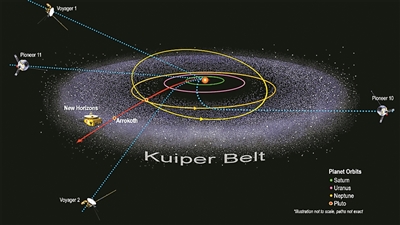
A road map of the most distant probes from humanity to fly out of the solar system.

An artist's impression of one of Voyager's "twin flower" probes. Image source for this article: US Space Network
Since the launch of the Pioneer 10 probe in 1972, there have been five spacecraft heading out of the solar system. They are Pioneer 10, 11, Voyager 1, 2 and New Horizons. These detectors have completed their original missions, but they have not died down. Some are still "working overtime" to detect more secrets of the universe for human beings; Move forward with established goals. In a recent report, the US Space Network sorted out the current status of these detectors.
Voyager "working overtime"
In 1977, the Voyager probes with different missions set sail one after another and started their own adventures. In 2022, the Voyager mission will mark its 45th anniversary. From flybys of multiple planets at close range to exploring the furthest distances humans have traveled in space, the twins have made enormous contributions to enhancing our understanding of the solar system.
In 1990, after the successful completion of the Voyager 1 mission, in order to save energy, scientists let it look back at the earth for the last time before rushing into the distance, and turned off its camera after taking the famous "dark blue spot" photo, but the spacecraft Other instruments on board are still collecting data from the sun's plasma and magnetic field.
In 2012, Voyager 1 flew out of the heliopause, escaped the influence of the solar wind, and flew out of the solar system. It became the farthest man-made probe and reached a distance of 23 billion kilometers from the earth. It is currently carrying Human information is heading further into the depths of the universe. In 1986, Voyager 2 arrived at Uranus, becoming the first probe to visit Uranus. In 2018, Voyager 2 also flew out of the heliopause and flew towards the farther edge of the solar system.
However, this pair of "sister flowers" only left the heliosphere, and it would take at least tens of thousands of years to fly out of the solar system. Their main mission now is to explore where the influence of the sun ends and the influence of other stars begins.
The edge of the solar system is also full of surprises. Scientists previously believed that the plasma from the sun would become more sparse and dispersed when leaving the center of the solar system, but in fact, astronomers still feel that the Voyagers encountered denser plasma after crossing the heliopause. Confused.
Pioneer has lost contact
The Pioneer 10 probe launched in 1972 and the Pioneer 11 probe launched in 1973 are of pioneering significance in the history of space exploration.
Pioneer 10 was the first probe to successfully traverse the asteroid belt and the first to observe Jupiter at close range, and it later flew by Saturn. Since Pioneer 10 was launched a little earlier, it used to be the farthest probe from the earth. Before it completely lost contact with the earth in 2003, it was about 12.23 billion kilometers away from the earth. This distance was later replaced by Voyager 1. beyond.
The fuel carried by Pioneer 10 has long been exhausted, and it is currently flying towards the outer solar system by inertia. If there is no accident, it is expected to reach Aldebaran, which is about 68 light-years away from the earth, in about 2 million years.
On April 6, 1973, Pioneer 11 was launched into space and reached the orbit of Saturn after 6 years of flight, becoming the first human probe to study Saturn and its rings. In September 1995, NASA terminated contact with Pioneer 11 in order to save the weakening power of Pioneer 11. Like Pioneer 10, it will move forward alone in the next long journey.
New Horizons is formidable
New Horizons is the youngest sibling of missions to fly out of the solar system, launched in 2006 to explore Pluto and its moons. After flying past Pluto in 2015, New Horizons has been leaving the solar system at record speed and is expected to reach the heliopause around 2040.
One of New Horizons' most significant discoveries was the confirmation of the existence of the Kuiper Belt. In 2019, New Horizons successfully flew over the "sky", the most distant celestial body known so far from the earth. It is about 6.4 billion kilometers away from the earth and belongs to the most primitive celestial body in the Kuiper belt. This is New Horizons' first mission extension.
Earlier this year, the spacecraft entered hibernation mode and is expected to remain dormant until March 1, 2023. After that, the research team plans to launch New Horizons' second Kuiper Belt Extension mission.
Meanwhile, the mission team is making some exciting new observations as they prepare to use New Horizons as a powered observatory in the distant solar system, providing information not available on Earth.
When New Horizons wakes up from hibernation to continue its journey, it will pass through the "Kuiper Gap," where scientists believe there are far fewer large Kuiper Belt objects, but it's not clear why.
During the extended mission, New Horizons will be able to better measure light and cosmic rays in space, track the distribution of dust across the solar system, and gain important information about the sun's influence, the research team said, complementing those obtained by Voyager. information. Because three powerful probes, Voyager and New Horizons, are flying in different directions, astronomers can use them to map irregularities in the solar system's structure.
(Original title "Voyager and New Horizons "working overtime" Pioneer has lost contact
What is the status of the five most distant probes from the earth? ")
